Private equity funds are liquidity pools of capital to be bought business that represent a chance for a high rate of return. They include a set financial investment horizonReturn on Investment (ROI), typically varying from four to 7 years, at which point the PE company wishes to profitably exit the financial investment.
2. Buyout or Leveraged Buyout (LBO)Contrary to VC funds, leveraged buyout funds invest in more fully grown businesses, usually taking a managing interest. Tyler Tysdal’s latest book LBOLeveraged Buyout (LBO) funds utilize extensive amounts of utilize to enhance the rate of return. Buyout discovers tend to be considerably larger in size than VC funds. Exit Factors to consider, There are numerous aspects in play that affect the exit technique of a private equity fund.
Private Equity: Overview, Guide, Jobs, And Recruiting
In terms of a wholesale exit from the business, there can be a trade sale to another buyer, LBO by another private equity firm, or a share repurchase. In terms of a partial exit, there could be a personal placement, where another investor purchases a piece of the business. Another possibility is corporate restructuring, where external financiers get included and increase their position in business by partially getting the private equity firm`s stake.
To keep knowing and advancing your profession, the list below resources will be practical:.
Developing A Private Equity Fund Foundation And Structure
Looking into your household history with Ancestry!.?.!? PE-backed. However what precisely is private equity? A foundational concept for anyone interested in learning aboutor working in a market tangential tothe personal markets, this blog site breaks down the essentials of PE. What is private equity? Private equity (PE) is a type of funding where money, or capital, is invested into a business.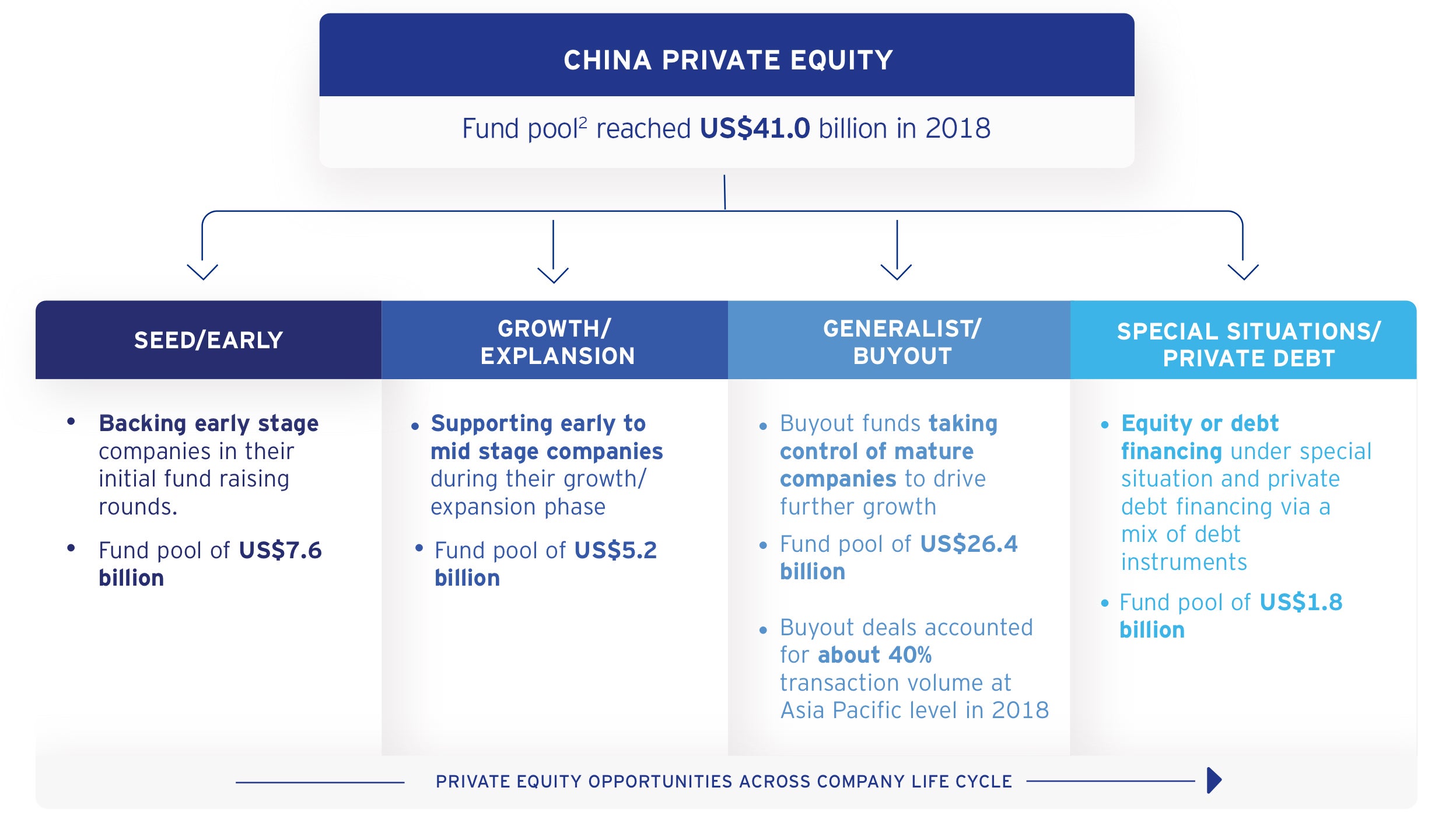 Islamic Private Equity Fund Structure Download Scientific Diagram
Islamic Private Equity Fund Structure Download Scientific Diagram
PE is a significant subset of a bigger, more complex piece of the monetary landscape called the personal markets. Private equity is an alternative property class along with real estate, equity capital, distressed securities and more. Alternative possession classes are considered less traditional equity investments, which indicates they are not as easily accessed as stocks and bonds in the public markets.
What Is Private Equity (Pe)? – Business Standard
What is a private equity fund? To purchase a company, private equity investors raise pools of capital from minimal partners to form a fundalso referred to as a private equity fund. Once they have actually hit their fundraising goal, they close the fund and invest that capital into promising business. Both private equity funds and hedge funds are restricted to recognized financiers.
And shared funds are just enabled to gather management charges, whereas PE funds can collect efficiency fees, which is gone over more listed below. How do private equity firms earn money? PE funds collect both management and efficiency costs. These can differ from fund to fund, however the. Computed as a percentage of possessions under management or AUM, typically around 2%.
Considerations For Raising Your Own Private Equity Fund
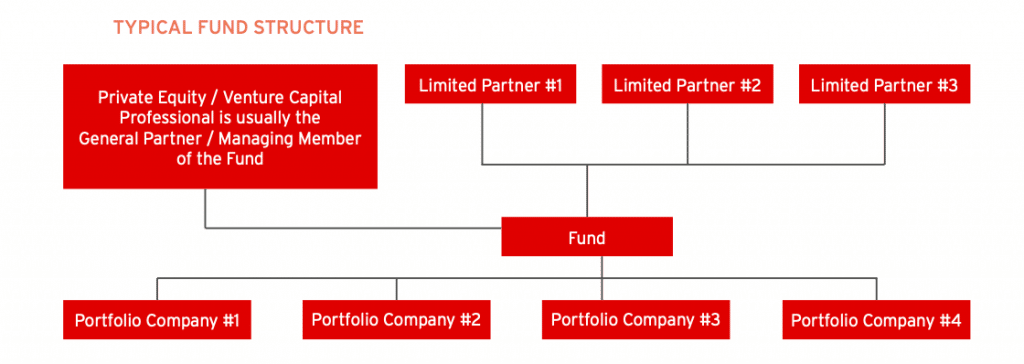 Private Equity Fund Structure ASimpleModel.com
Private Equity Fund Structure ASimpleModel.com 
Private Equity Definition: How Does It Work?
Determined as a portion of the revenues from investing, typically around 20%. These charges are planned to incentivize higher returns and are paid out to employees to reward their success. How does private equity work? To invest in a business, private equity investors raise pools of capital from restricted partners to form the fund.
When a PE firm sells one of its portfolio companies to another business or financier, the firm typically makes a revenue and distributes go back to the limited partners that purchased its fund. Some private equity-backed companies may also go public. What are some examples of private equity firms? The Blackstone Group Headquartered in New York City, the investment firm buys PE, real estate and more.
Aua Private Equity: Home
So, VC is a type of private equity. Here are some extra distinctions between PE and VC. Private equity PE firms frequently buy fully grown businesses in standard markets. Utilizing capital devoted from LPs, PE financiers invest in promising companiestypically taking a majority stake (> 50%). When a PE firm sells one of its portfolio companies to another business or investor, returns are distributed to the PE investors and to the LPs.
Venture capital VC firms typically buy tech-focused start-ups and other young companies in their seed. Using dedicated capital, VC financiers typically take a minority stake
